Unveiling the Distinctions: Articulating Boom, Vertical Lift, and Telescopic Boom Aerial Work Platforms
In modern construction, industrial maintenance, and municipal engineering, aerial work platforms (AWPs) have become indispensable, acting as mechanical guardians that ensure the safety and efficiency of high-altitude operations. Among these, the articulating boom, vertical lift, and telescopic boom AWPs stand out for their unique capabilities, each playing a pivotal role in different scenarios. But what exactly sets them apart?
I. Structural Design: Ingenious Mechanical Marvels
Articulating Boom AWP
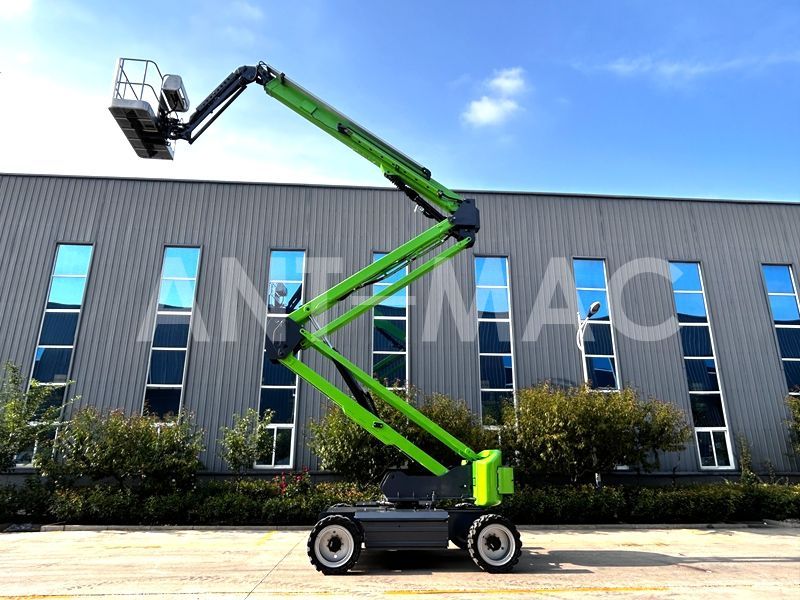

Often hailed as the "flexible dancer" of high-altitude operations, the articulating boom AWP features a multi-segmented arm structure. Constructed from high-strength alloy materials, its arms resemble precisely connected mechanical joints, linked by intricate hinge points that endow the machine with remarkable agility. When in operation, these segments can bend at various angles, deftly navigating around protruding building structures, crisscrossing pipelines, and other obstacles. This enables the platform to reach multiple work points from a single lift-off location, making it a master at handling complex spatial environments and an ideal choice for confined spaces.
Vertical Lift AWP
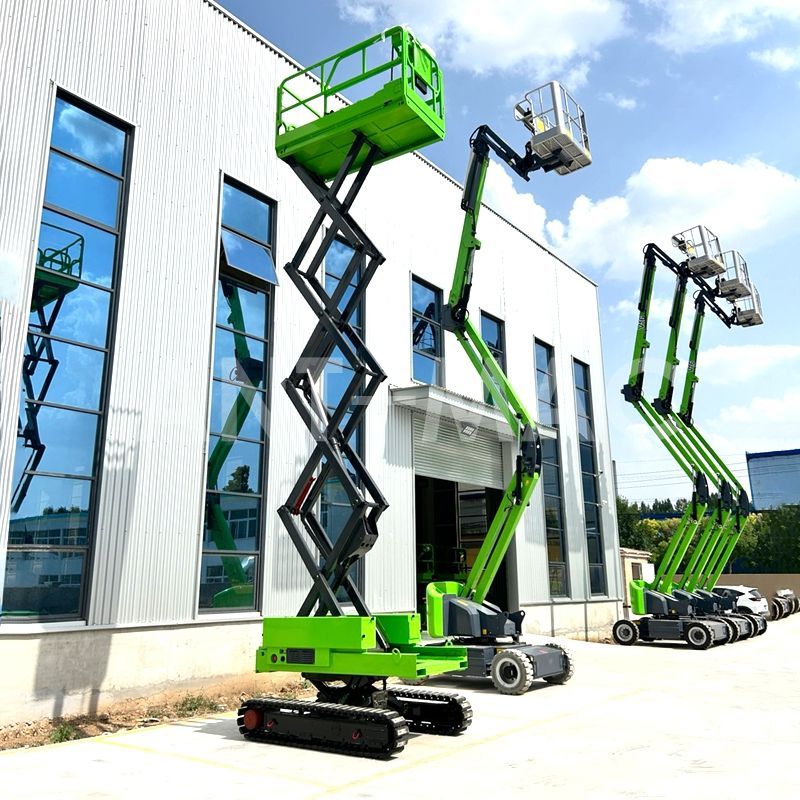

Renowned for its stability, the vertical lift AWP relies primarily on scissor or telescopic sleeve structures for vertical movement. The scissor-lift type features a cross-arranged linkage mechanism that resembles an open pair of scissors. As hydraulic cylinders drive the linkages to extend and retract, the platform ascends and descends smoothly. The telescopic sleeve design, on the other hand, functions like a collapsible telescope, with multiple nested sleeves. These sleeves are actuated by hydraulic systems or wire rope pulley mechanisms, facilitating vertical displacement. Typically equipped with spacious work platforms and robust support structures—akin to a sturdy chassis—vertical lift AWPs ensure steadfast stability during operation. However, their vertical-only movement inherently limits their maximum working height.
Telescopic Boom AWP
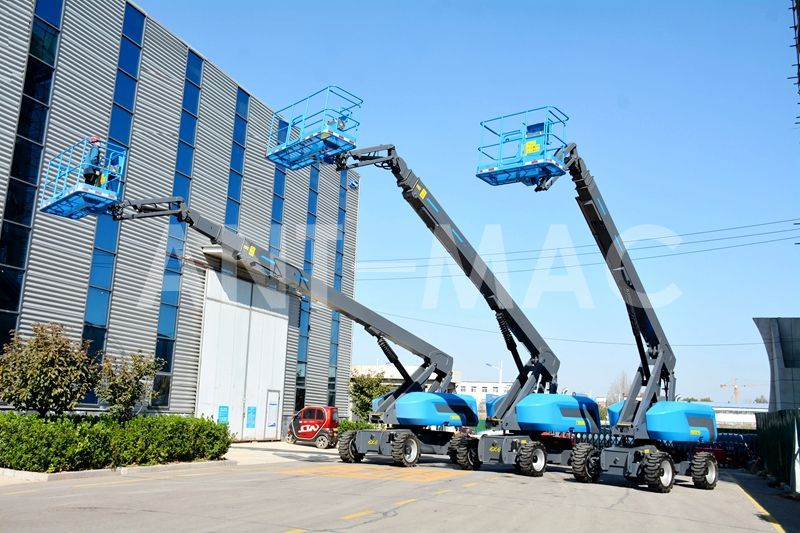

Resembling an infinitely extendable "mechanical arm," the telescopic boom AWP comes in two main variants: straight-boom and articulated-boom. The straight-boom version comprises multiple nested sleeves that extend and retract hydraulically, either synchronously or asynchronously, allowing it to achieve astonishing vertical reach. The articulated-boom variant adds a foldable joint at the end of the straight arm, enabling both height extension and angular adjustment. Whether straight or articulated, these booms offer significant working heights and lateral outreach, earning them the title of "long-range pioneers" in high-altitude operations.
II. Operational Principles: The Intricacies of Precision Mechanics
Articulating Boom AWP
The articulating boom AWP draws its power from hydraulic cylinders integrated into each arm segment, acting as the "muscles" that energize the mechanical limbs. When an operator issues commands, the hydraulic system responds promptly, with cylinders pushing or pulling the arms to control the folding and unfolding angles of each segment. Coupled with a rotating mechanism, the platform can achieve a full 360-degree rotation. This precision control allows the articulating boom AWP to effortlessly traverse obstacles and reach target work positions with pinpoint accuracy, almost as if guided by intelligent vision.
Vertical Lift AWP
For scissor-lift AWPs, the lifting principle hinges on the extension and retraction of hydraulic cylinder rods. When hydraulic fluid is pumped into the cylinders, the rods extend, pushing the cross linkages to change angles and lift the platform. Conversely, retracting the rods lowers the platform. The process mimics the opening and closing of scissors, ensuring smooth and stable movement. Telescopic sleeve AWPs, meanwhile, rely on hydraulic systems or wire rope pulley setups to drive the sequential extension and retraction of the nested sleeves. In hydraulic systems, fluid pressure moves pistons to slide the sleeves, while wire rope systems use motors to wind and unwind ropes, guaranteeing steady vertical movement.
Telescopic Boom AWP
With hydraulic fluid serving as its "lifeblood," the telescopic boom AWP uses hydraulic cylinders to extend and retract its boom. When the hydraulic system activates, fluid enters the cylinders, propelling the piston rods and extending or retracting the boom's nested sleeves. For articulated-boom models, additional independent cylinders control the bending angle of the foldable end segment. High-end versions often feature automatic platform leveling systems and Hall-effect proportional control handles. These allow operators to adjust the boom's position and angle with millimetric precision—simply by manipulating the handle, the machine responds accurately to every command.
III. Application Scenarios: Specialized Workhorses
Articulating Boom AWP
The articulating boom AWP's flexibility makes it the go-to choice for environments with tight spaces and numerous obstacles. In urban settings, when maintaining the facades of aging buildings cluttered with air conditioning units and security grilles, this platform can effortlessly maneuver through the maze to safely position workers. Similarly, during power line maintenance, whether navigating the winding wires in mountainous areas or the crisscrossing cables between skyscrapers, its agile steering and obstacle-crossing capabilities ensure efficient task completion.
Vertical Lift AWP
Vertical lift AWPs shine in indoor applications and tasks with modest height requirements. In supermarkets, their large platforms accommodate multiple workers and equipment simultaneously, streamlining shelf installation and product placement. In sports arenas, the stable support and expansive working area allow technicians to safely replace lighting fixtures and clean the ceiling. While their height limitations restrict them from reaching extreme altitudes, in indoor, enclosed, and structured environments, their stability and spacious platforms offer unparalleled advantages.
Telescopic Boom AWP
Telescopic boom AWPs are the Main force in large-scale projects and high-altitude, long-reach operations. At shipyards, when constructing or repairing vessels dozens of meters tall, these platforms extend to the ship's peak, providing a secure workspace for workers. In bridge construction and maintenance, their extraordinary arm spans and lateral reach ensure comprehensive coverage, whether reinforcing piers or painting bridge decks. During the installation of steel structures in large venues, their towering height and precise operation capabilities enable accurate placement of components, playing a crucial role in the successful execution of major engineering endeavors.
Selecting the right aerial work platform requires a comprehensive assessment of factors including the work environment, required height, operational range, and budget. These three types of AWPs, each excelling in its domain, collectively safeguard the safety and efficiency of high-altitude operations, ensuring that no task, no matter how challenging, remains out of reach.
 Antmac's Chinese New Year Than
Antmac's Chinese New Year Than
 Building Absolute Stability: A
Building Absolute Stability: A
 Data Speaks: Antmac's After-Sa
Data Speaks: Antmac's After-Sa
 Industry Trendsetter: Antmac's
Industry Trendsetter: Antmac's
 Russian
Russian
